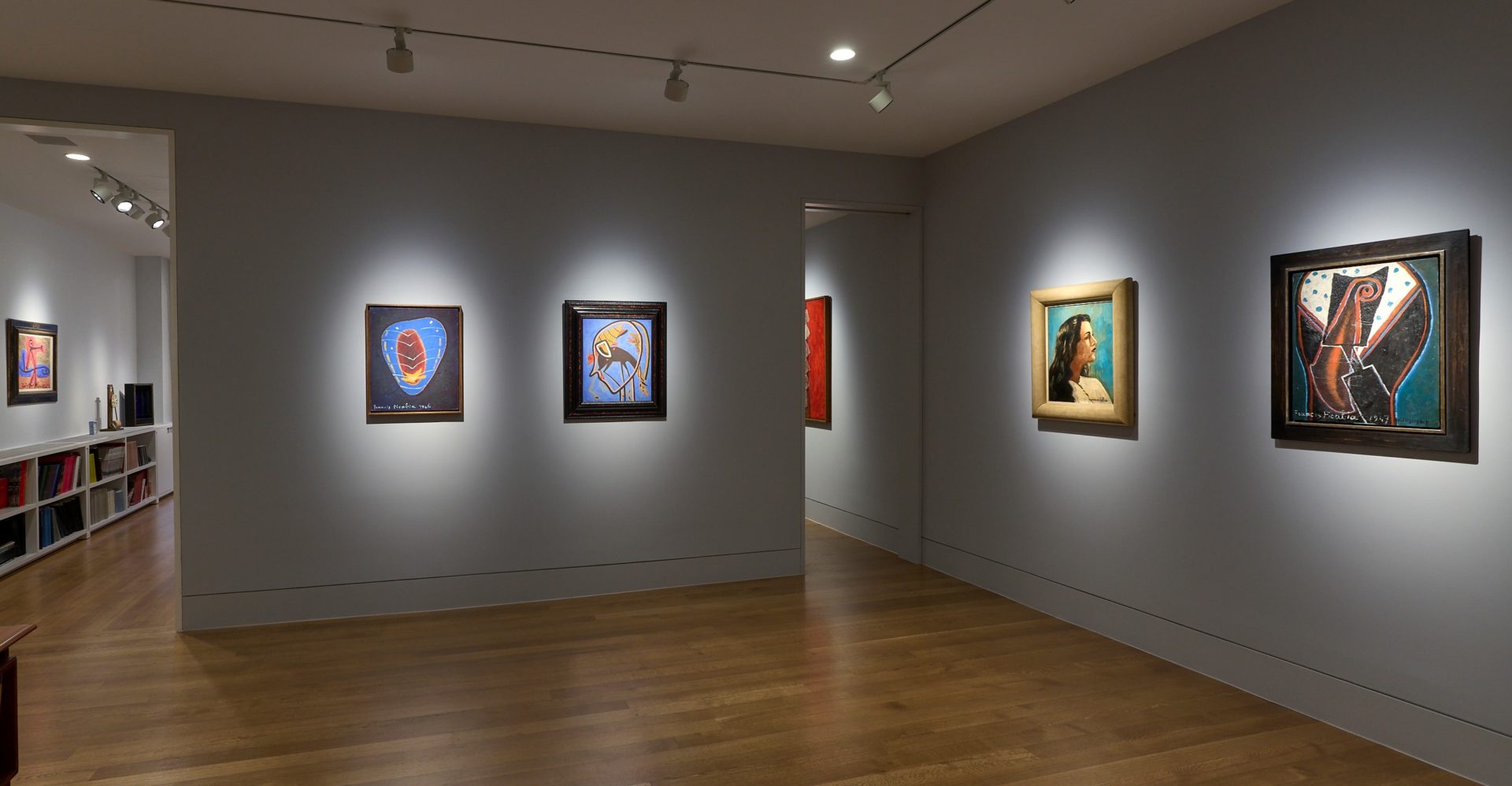
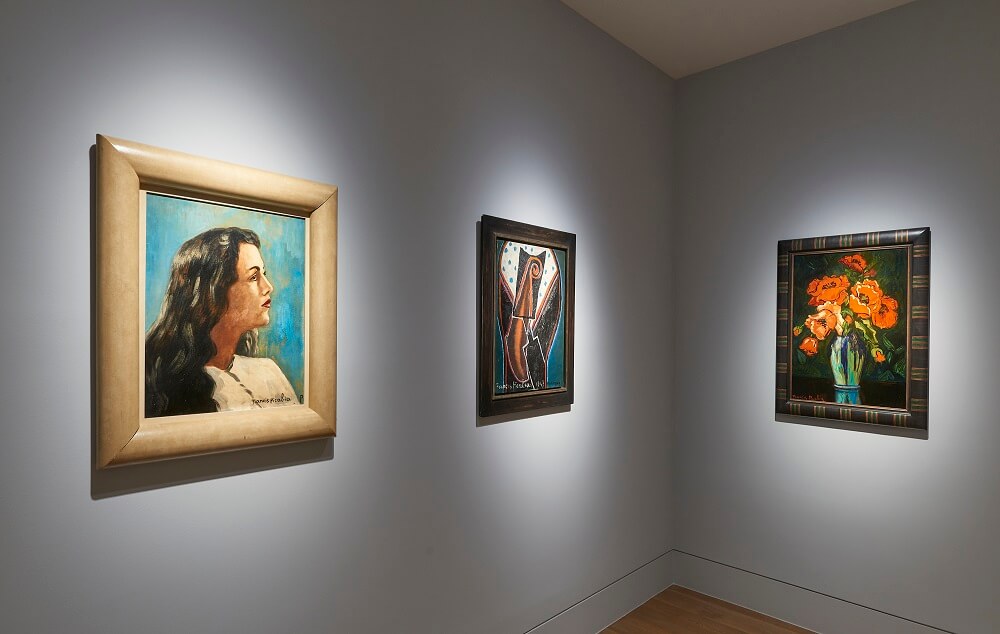
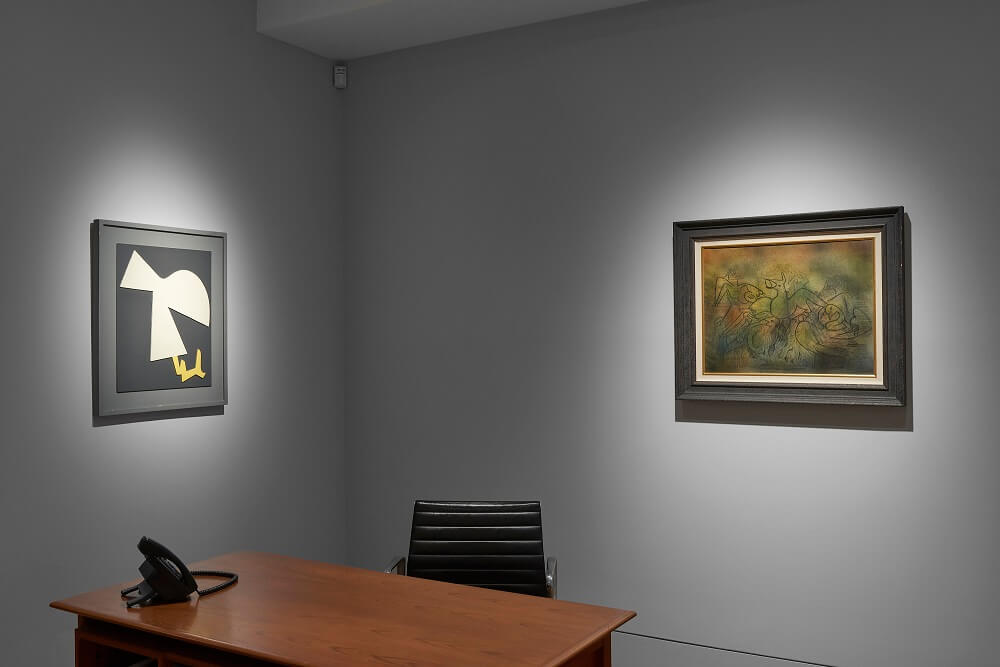
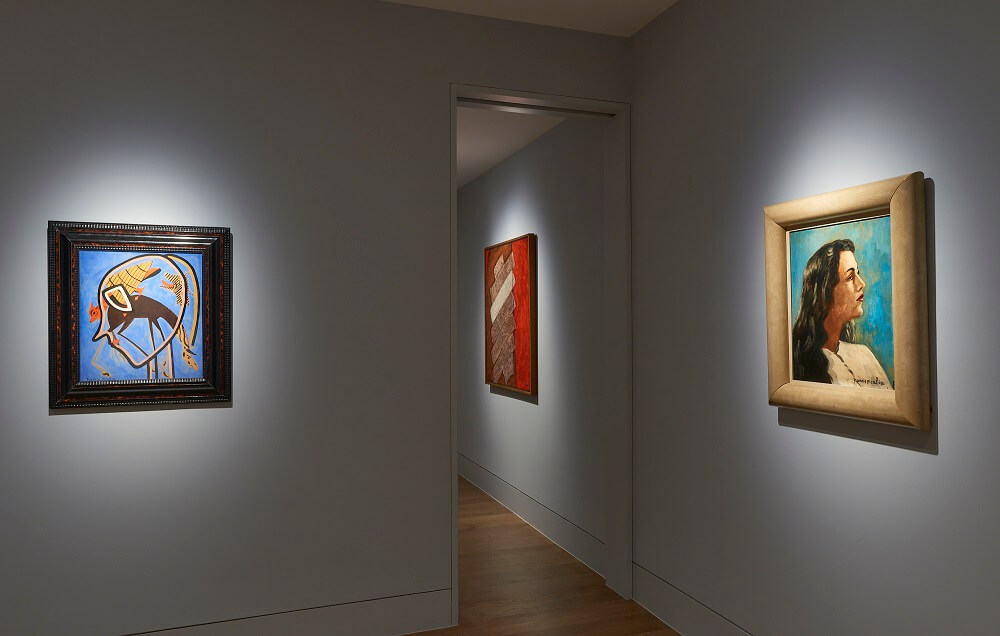
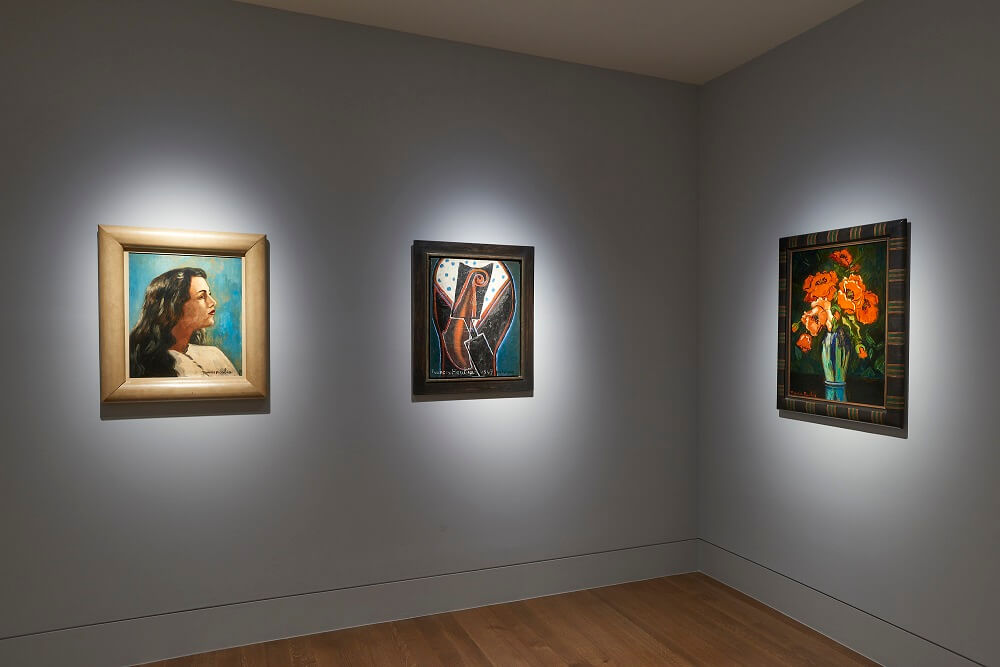
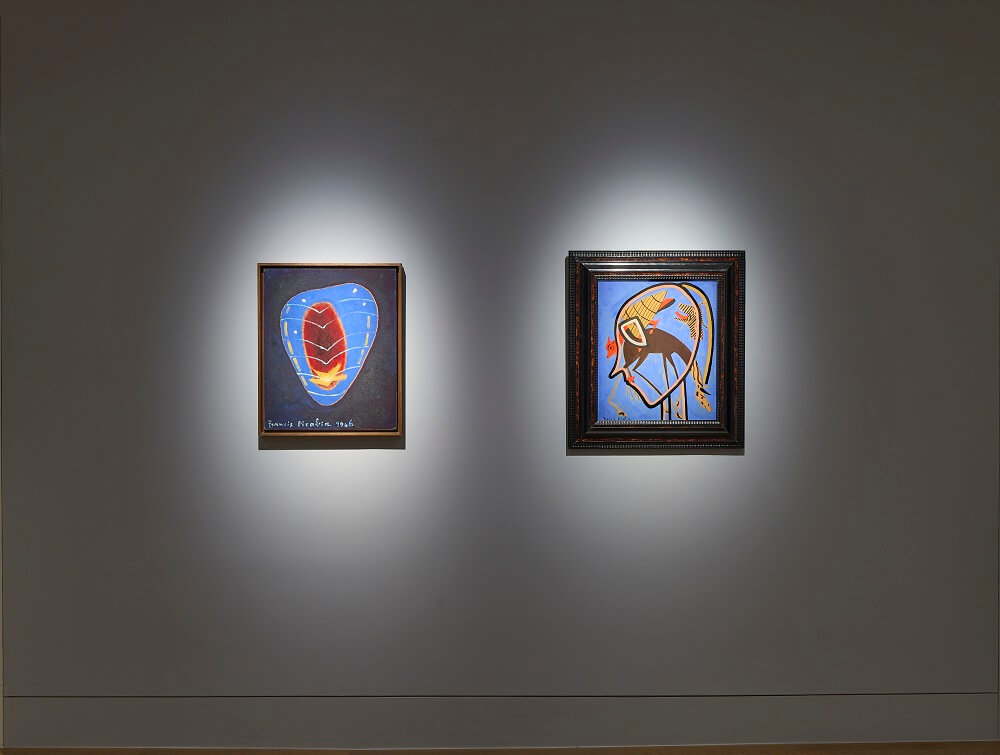
Francis Picabia was one of the most innovative and varied masters of early Modernism. His astonishing range drew on an apparently irrepressible urge to create, as painter, poet, set designer, publisher and graphic artist. In his ability to sublimate the structures of whichever avant-garde movement was in vogue to the whims of his creative unconscious it is perhaps with Surrealism that he can be most closely associated. Dickinson’s presentation of Picabia and the Surrealists showcases five characteristic paintings from the 1930s and 40s alongside works by his contemporaries Max Ernst, Jean Arp, Yves Tanguy, Paul Klee and André Masson, illustrating both Picabia’s impact on the movement and his importance for later generations of artists.
Picabia’s reputation has rarely been higher, as was demonstrated in the encyclopaedic 2016 retrospective at the Museum of Modern Art. Roberta Smith noted in her review of the show that “Picabia’s stature has grown. His work seems more alive today than that of any artist of his cohort, even Duchamp. … Picabia may play as crucial a role for our time as he did forhis own. He refused to choose between the two great factions of early modernism — one conceptual and linguistic and descended from Duchamp; the other, painterly and formal, from Picasso and Matisse. He loved both subversion and the physicality of making things too much to take sides.” (R Smith, ‘Modernism’s Playboy Prankster’, New York Times, 18 Nov. 2016, p. 21).
In the moody abstraction of Chenille (1946); the layering and sampling of Lano (1937-38), which recalls the Transparènces of the late 1920s; and the proto-Pop appropriation of the realist female portrait of 1942-43, derived from a pin-up photograph, the exhibition presents Picabia in his Protean variety. This facility was viewed with alarm by his contemporaries, who were already envious of his private income and fashionable lifestyle. In retrospect, the ability to shift between schools, styles and media mark him out as an apostle of postmodernism, and his influence can be seen in the work of artists such as Sigmar Polke, Julian Schnabel and Richard Prince.